Cleaning
Customers expect food booths to be clean and assume that you will handle their food safely. A clean and organized booth creates a good impression and helps to make a safe, pleasant environment for everyone. However, it is important to remember that even though the booth looks clean it could be contaminated so, once you have cleaned the cutting boards, dishes, utensil, equipment and counter tops with hot, soapy water and rinsed with water, you must sanitize all food contact surfaces. |
SANITIZING Sanitizing is the reduction of bacteria and viruses to a low, safe level. This can be achieved by the use of chemical sanitizers. Sanitizers must be used after cleaning and rinsing, because they cannot work in the presence of grease and dirt. Two common sanitizers used in food booths are:
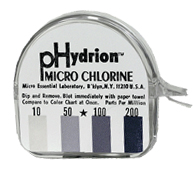
Chlorine is the most commonly used sanitizer. It kills most of the disease-causing bacteria and viruses that washing and rinsing leave behind. To prepare a sanitizing solution with the approved concentration of chlorine-base chemical sanitizer you first need to know the proper level of chlorine. This level is 100 parts per million (ppm). This ppm is a ratio of water and sanitizer, which has been determined to be an adequate level to sanitize food contact surfaces. The amount of sanitizer to be mixed depends on the concentration of the sanitizer solution so read the instructions.
Example: When using a 5.25% sodium hypo-chlorite liquid chlorine (commercial grade, non-perfumed) add ½ oz per gallon of warm water. |
Stir the sanitizer and water solution and dip a test strip paper into the diluted chlorine solution. Don’t shake or move the test strip paper. Remove and compare to color chart at once. It must read 100 ppm. See below for color code.
|
Quaternary Ammonia (“Quats”)
Stir the sanitizer and water solution and dip test strip paper into diluted Quat solution. Don’t move or shake test strip paper. Remove and compare to color chart after 10 seconds. It must read 200 ppm. This process must be repeated every time a sanitizer is prepared for use. California Required Sanitizer Concentrations and Contact Times: For chlorine sanitizer ensure the utensils are submerged in the sanitizer for a minimum of 30 seconds.
For "Quat" sanitizer ensure the utensils are submerged in the sanitizer for 60 seconds.
|
| Cleaning Cloths
To maintain the cleaning cloth in working condition you must do the following:
|
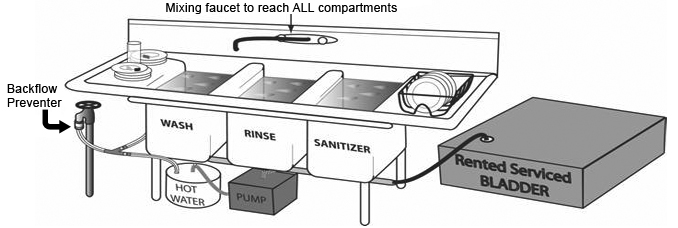
Utensil Washing Utensils and cutting boards must be properly washed, rinsed and sanitized using a three compartment sink either within the booth or shared by up to 4 booths handling open food, when provided by the event organizer. The 3-compartment sink may be placed outside the booth but shall have over-head protection. The sinks shall be large enough to accommodate the largest utensil. The 3-compartment sink must have two drain boards. The first drain board is to be used for soiled utensils. The second drain board is to be used for air-drying clean, sanitized utensils.
|
Physical And Chemical Contamination Physical hazards include dirt, hair, broken glass, shell or bones, and other objects. The following are food safety controls:
Chemical hazards include: detergents, cleaning and sanitizing agents and other similar chemicals. Keep them labeled and away from food and food related surfaces. The following are food safety controls:
|