Food ProtectionFood must be properly handled because bacteria may be present on products when you purchase them. Plastic-wrapped boneless chicken breasts and ground meat, for example, were once part of live chickens or cattle. Raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs are not sterile. Neither is fresh produce such as tomatoes, sprouts, and melons. Foods, including safely cooked, ready-to-eat foods, can become cross contaminated with bacteria transferred from raw products, meat juices or other contaminated products, or from food handlers with poor personal hygiene. So, you need to control the conditions that enable bacteria to grow and multiply. Bacteria need:
Moist, protein-rich foods are called Potentially Hazardous Foods (PHFs). Examples of PHFs:
Examples of nonPHFs:
|
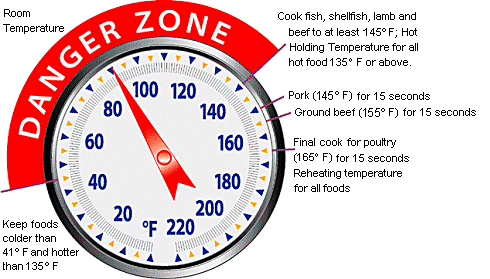
Bacteria multiply faster in a specific temperature range. This temperature range is 45°F to 135°F and is called the Danger Zone. So you need to minimize the time food is in the Danger Zone.
|